
Behavior Change models condense many years of research on the influences shaping our actions. In healthcare market research, there continues to be significant focus on COM-B, given its wide applicability. We should not, however, overlook the potential contribution of other models. For example, the Health Belief Model (Rosenstock, 1974, updated by Becker, 1977) and the Socioecological Model (Bronfenner, 1979) each provide important perspectives on the influences on health behaviors.
The Health Belief Model focuses on patients’ inner beliefs, triggers, and motivations, while the Socioecological Model focuses on the external and societal influences. Combining these different perspectives allows us to understand patient health behaviors more holistically. Providing a stronger basis to understand the patient experience – and to design behavior change interventions that are likely to be effective.
The Health Belief Model dives deep into the personal factors supporting health behaviors
As shown in the diagram below, the Health Belief Model focuses on three core strands:
- Patient beliefs about their health risks
- Patient beliefs about treatments (or other health behaviors)
- The factors impacting their health behaviors
Each of these strands has two elements, which, together, provide a comprehensive understanding of factors guiding patient health behaviors and the opportunities to change them.
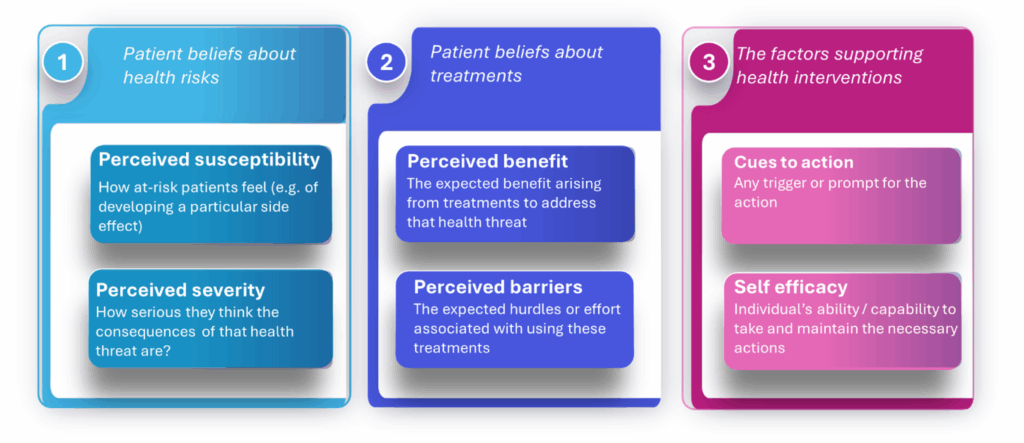 Diagram 1 – the Health Belief Model
Diagram 1 – the Health Belief Model
As an example, we could consider the factors that might influence patient willingness to use a chronic weight management treatment.
| Criteria | Example considerations |
| Perceived susceptibility |
|
| Perceived severity |
|
| Perceived benefit |
|
| Perceived barriers |
|
| Cues to action |
|
| Self-efficacy |
|
The Socioecological Model: the external influences shaping health behaviors
The Socioecological Model focuses on the societal factors guiding behaviors. It helps us recognize both the variety of external influences and their respective strengths. Some (such as government and legal restrictions) have significant influence but may not be experienced directly – patients may be more aware of family members, friends, or social media influencers. Given the importance of societal influences on health and treatment decisions, for example, as we found in our recent self-funded study: The Power of Words: In sickness and in health, this model gives a framework in which external influences can be understood.
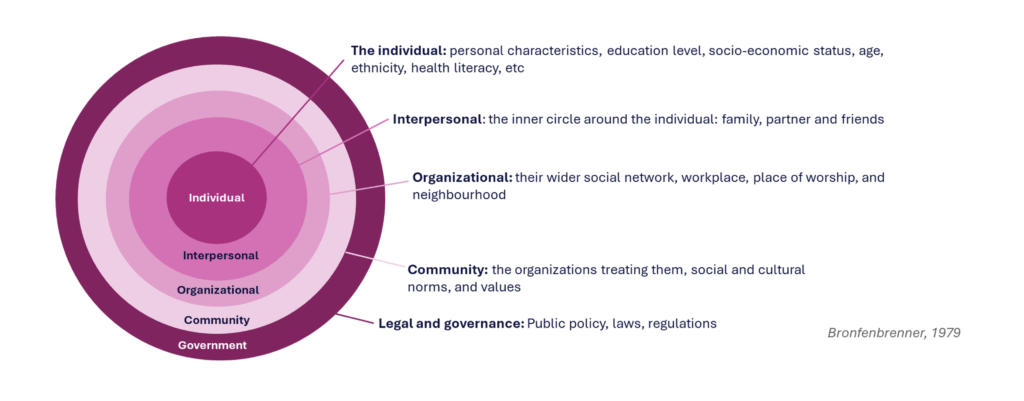 Diagram 2 – the Socioecological Model
Diagram 2 – the Socioecological Model
Again, using chronic weight management as an example, we can see the model leads us to focus on different but complementary factors in our assessment:
| Criteria | Example considerations |
| Individual |
|
| Interpersonal |
|
| Community |
|
| Organizational |
|
| Governmental |
|
This summary of these two behavioral models shows how they could shape a deep understanding of the factors influencing weight and weight management. The Health Belief Model and Socioecological Model – both relatively simple to understand – remind us to consider a wide range of powerful influences on health behaviors. Taken together, they provide a comprehensive framework for assessing the factors affecting health behaviors and give our clients a solid foundation to assess possible behavior change options.
Chat to our Beyond Behavior team about how these two models could help you unearth a powerful range of influences.
